

Image modified from Hannes Grobe, Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, vectorised by User:Lichtspielderivative work: Lichtspiel (Ocean-birth_hg.png), via Wikimedia Commons. 17 Oceanic transform plate boundaries and fracture zones Transform plate boundary Transform plate boundaries in the ocean basins are prominent linear. Yet they undergo devastating earthquakes such as the 2010 Haiti disaster because of the sliding Caribbean Plate. They don’t have notable features like large chains of mountains. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. Transform plate boundaries are one of the 3 plate tectonic boundary types along with divergent and convergent plate types. As the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. Divergent plate boundaries, showing plates moving away from each other. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundariesdivergent, convergent, and transform. We can see the relative motion of these boundaries in cross-sections, or slices through Earth: Figure 1. There are three types of plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform boundaries. We already investigated the topography of plate boundaries in a previous chapter: Applications: Plate Tectonics Review: The Three Types of Plate Boundaries Interpret the type of plate boundary based upon motion shown in cross-sectional or map view.The San Andreas Fault is one of the best examples of lateral plate motion. Shear stress is experienced at transform boundaries. When two tectonic plates slide past each other, the place where they meet is a transform or lateral fault. Tensional stress happens at divergent plate boundaries where two plates are moving away from each other. This can lead to the formation of huge, high mountain ranges such as the Himalayas. Put your graham crackers side by side again, so they are touching. Since neither plate is stronger than the other, they crumple and are pushed up. These are boundaries where two plates move past each other. About 80% of earthquakes occur where plates are pushed together, called convergent boundaries.Īnother form of convergent boundary is a collision where two continental plates meet head-on. Sometimes the molten rock rises to the surface, through the continent, forming a line of volcanoes. A transform plate boundary is a margin between two lithospheric plates that constitutes a regional-scale transform fault. The rocks pulled down under the continent begin to melt.
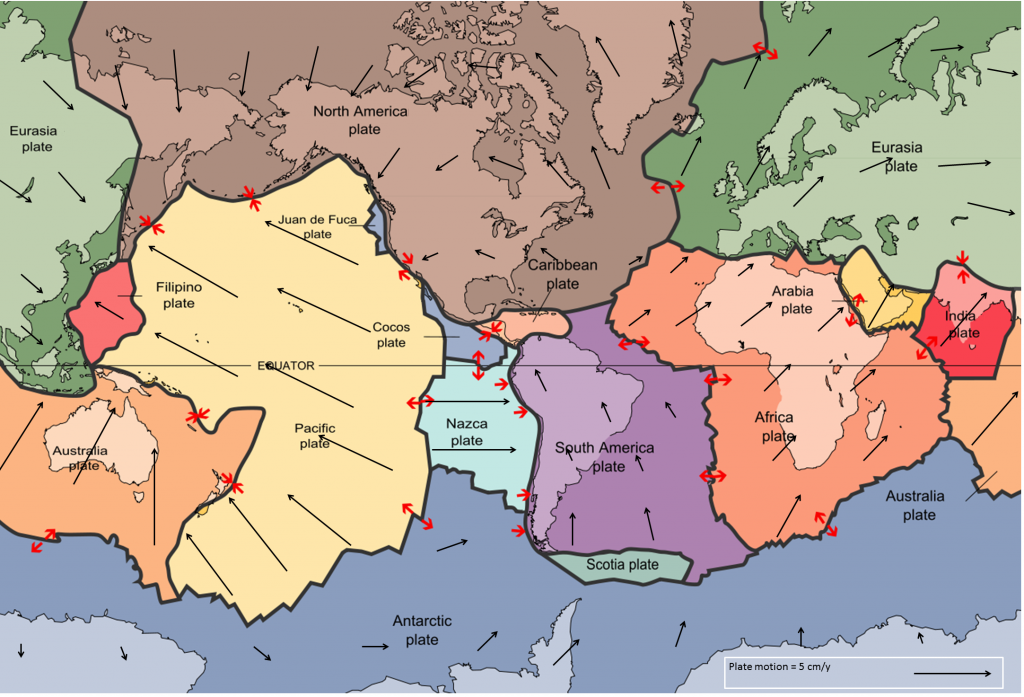
Subduction causes deep ocean trenches to form, such as the one along the west coast of South America. When a continental plate meets an oceanic plate, the thinner, denser, and more flexible oceanic plate sinks beneath the thicker, more rigid continental plate. The Great Rift Valley in Africa, the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden all formed as a result of divergent plate motion.Ĭonvergent (Colliding): This occurs when plates move towards each other and collide. The earthquakes that occur along these zones, called spreading centers, are relatively small. Molten rock from the mantle erupts along the opening, forming new crust. Transform plate boundaries, also known as conservative plate boundaries, occur where lithospheric plates slide past each other and where the crust is. The three main types of plate movements include:ĭivergent (Spreading):This is where two plates move away from each other. The movements of the plates help shape the geological features of our planet. Other plates include continents, and some plates include both continents and ocean.

There are three types of plate boundaries or zones, each of which features a different type of plate interaction. The meaning of TRANSFORM FAULT is a strike-slip fault that occurs typically between segments of a mid-ocean ridge or other tectonic-plate boundary and that. They are, however, much more complex than that. Some of the plates have ocean water above them. Transform boundaries are areas where the Earth's plates move past each other, rubbing along the edges. transform fault, in geology and oceanography, a type of fault in which two tectonic plates slide past one another. When the plates finally give and slip due to the increased pressure, energy is released as seismic waves, causing the ground to shake. Most seismic activity occurs at three types of plate boundaries-divergent, convergent, and transform.Īs the plates move past each other, they sometimes get caught and pressure builds up. Movement in narrow zones along plate boundaries causes most earthquakes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
